Practice Update – March 2025
How to master employer obligations in 2025
Taxpayers who employ staff should remember the following important dates and obligations:
Fringe benefits tax (FBT)
31 March 2025 marks the end of the 2024-25 FBT year. Employers should remember the following regarding their FBT tax time obligations.
- They should identify if they have provided a fringe benefit. If they have, they should determine the taxable value to work out if they have an FBT liability.
- They should lodge an FBT return and pay any FBT owed by 21 May 2025. If their registered tax agent lodges electronically for them, they have until 25 June 2025.
- They should keep the right records to support their FBT position.
Pay as you go (PAYG) withholding
Taxpayers need to withhold the right amount of tax from payments they make to their employees and other payees, and pay those amounts to the ATO.
Single touch payroll (STP)
Employers should finalise their STP data by 14 July 2025 for the 2024/25 financial year (there may be a later due date for any closely held payees).
Super guarantee (SG)
- 28 January, 28 April, 28 July and 28 October are the quarterly due dates for making SG payments
- The SG rate is currently 11.5% of an employee's ordinary time earnings. From 1 July 2025, it will increase to 12.0%.
- Taxpayers should ensure SG for their eligible employees is paid in full, on time and to the right super fund, otherwise they will be liable for the SG charge.
ATO's tips to help taxpayers stay on top of their BAS
The ATO has the following tips to help taxpayers get their BAS right before they lodge:
- They should make sure they enter the figures for their obligations at the correct label, and only complete applicable fields.
- If lodging online, or through a registered tax or BAS agent, they may be able to get an extra 2 or 4 weeks to lodge and pay.
- If they have nothing to report for the period, they can lodge a 'nil' BAS online by selecting 'Prepare' and then 'Prepare as nil', or they can call the ATO's automated service "any time of the day".
- If they made a mistake on their last BAS, instead of lodging a revision, they may be able to use their current BAS to fix it. For example, they can use label 1A to adjust GST on sales, or label 1B to adjust GST on purchases.
- They can also use their BAS to vary an instalment amount.
Claiming fuel tax credits when rates change
Fuel tax credits changed on 3 February, and taxpayers could receive more savings for fuel they have acquired on and from this date. Different rates apply based on the type of fuel, when it was acquired and what activity it is used for.
The ATO has the following tips for taxpayers to ensure they are claiming correctly.
- They can use the ATO's 'eligibility tool' on its website to find out if they can claim fuel tax credits for fuel they have acquired and used.
- They can use the ATO's online fuel tax credit calculator (which should automatically apply the right rate) to work out their claim.
- They can lodge their BAS via Online services or a registered tax or BAS agent (lodging via an agent can allow them extra time to lodge and pay).
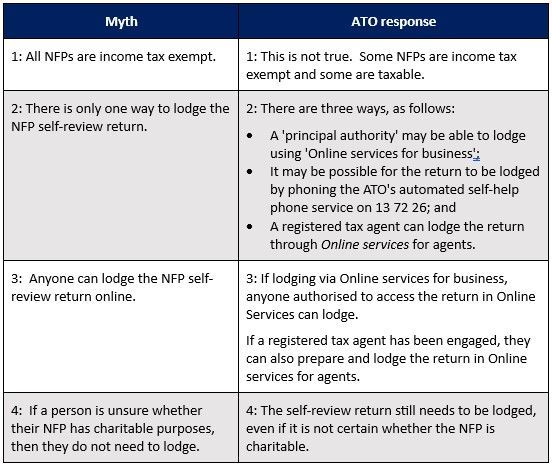
ATO "busts" Not-For-Profits myths
As the Not-for-profit (NFP) self-review return is due in March, the ATO has recently published a document 'busting' various NFP 'myths'.
Taxpayer's claim for input tax credits unsuccessful
In a recent decision, the Administrative Review Tribunal (ART) rejected a taxpayer's claim for input tax credits on the basis that all the relevant GST returns (ie. BASs) were lodged out of time.
For the GST periods from 1 October 2015 to 31 March 2017, the taxpayer filed each of her GST returns more than four years after they were due. The taxpayer still claimed input tax credits totalling over $10,000 for this period.
The ATO disallowed this claim, on the basis that none of the input tax credits were claimed within the four-year period, as required by the GST Act.
The ART upheld the ATO's decision, noting that, as the taxpayer did not file the GST returns within the four-year period "she did not have input tax credits taken into account . . . As a consequence, . . . (she) simply ceased to be entitled to those input tax credits."
ATO's appeal against decision that UPEs are not "loans" fails
The Full Federal Court recently dismissed the ATO's appeal against an AAT decision that unpaid present entitlements (UPEs) owing by a trust to a corporate beneficiary were not "loans" for Division 7A purposes.
A corporate beneficiary had become entitled to a share of the income of a trust for the 2013 to 2017 income years. Parts of these entitlements remained outstanding, resulting in UPEs. The ATO treated these UPEs as loans from the corporate beneficiary back to the trust (and, in consequence, as "deemed dividends" made to the trust).
The AAT held at first instance that a loan had not been made in this case.
The Full Federal Court upheld the AAT's decision, noting that a loan for Division 7A purposes requires an obligation to repay an amount, not merely the creation of an obligation to pay an amount (such as when a trust distributes income to a beneficiary).
We recently prepared a detailed Tax Alert on the Bendels Case decision, to read click here.
Please do not hesitate to contact your Lowe Lippmann Relationship Partner if you wish to discuss any of these matters further.
Liability limited by a scheme approved under Professional Standards Legislation
